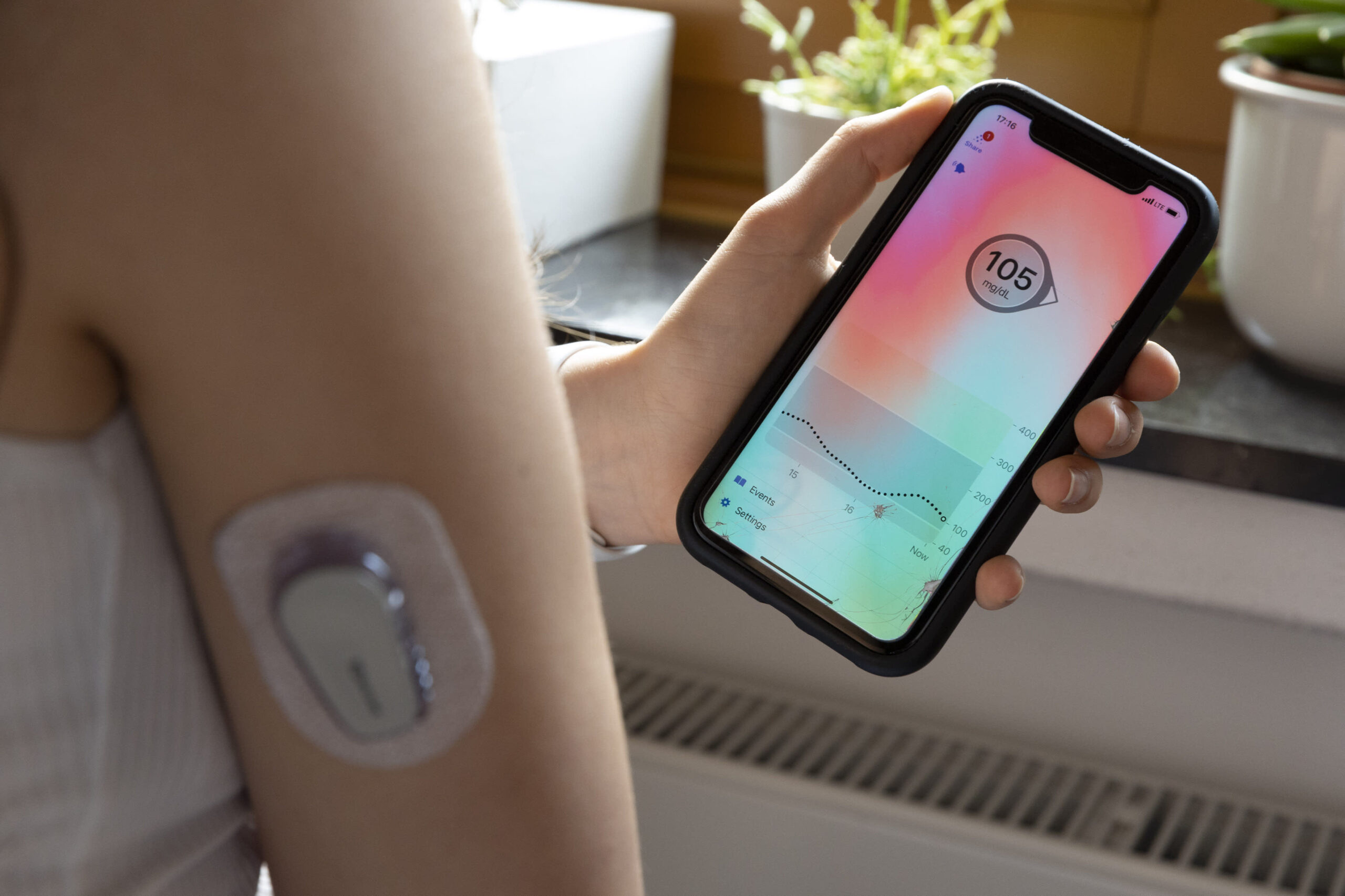
Imagine a world where managing a complex health condition such as diabetes meant endless guesswork and constant uncertainty. Thankfully, that era is rapidly fading into the past. Over recent decades, the landscape of diabetes care has been revolutionized, shifting dramatically from basic monitoring to sophisticated technological solutions. For the millions of individuals navigating life with diabetes in the U.S., the tools chosen for daily management are profoundly impactful. Among the most transformative innovations are insulin pumps and Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs). These groundbreaking devices have redefined diabetes management, providing unprecedented precision and newfound freedom. This leads to a fascinating question: within the dynamic U.S. diabetes device market, which is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 6.91% during the forecast period. And what factors contribute to the sustained leadership of the U.S. in this vital field?
Insulin Pumps vs. CGMs: A Market Overview
Both insulin pumps and CGMs address vital aspects of diabetes care. Insulin pumps deliver continuous insulin doses, mimicking the pancreas and aiming for better glycemic control. CGMs, on the other hand, provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day and night, eliminating the need for frequent fingerstick tests. This constant data flow empowers individuals and their healthcare providers to make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.
Tethered pumps currently hold a larger market share, although tubeless patch pumps are gaining traction due to their convenience. Companies such as Medtronic, Tandem, and Insulet with its Omnipod system are prominent players in this space. The adoption of CGM systems is accelerating, driven by increased awareness, favorable reimbursement policies, and improved clinical data validating their effectiveness in reducing long-term complications.
While insulin pumps have been a cornerstone of intensive diabetes management for years, particularly for individuals with Type 1 diabetes, the rapid growth and widespread adoption of CGMs, even among some Type 2 diabetes populations, suggest a potential shift. The immediate, actionable data provided by CGMs is proving to be a game-changer, fostering a proactive approach to blood sugar management. The integration of these two technologies, creating “closed-loop” or “artificial pancreas” systems, represents the pinnacle of current innovation, automatically adjusting insulin delivery based on CGM readings. For instance, Insulet’s Omnipod 5 Automated Insulin Delivery System is now FDA-cleared for U.S. adults with type 2 diabetes. It is the first and only AID system cleared for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, expanding access to approximately 6 million insulin-requiring individuals. Clinical data showed significant improvements in health outcomes.
Why the U.S. Is the Global Leader in Diabetes Device Innovation?
Several factors contribute to the U.S. maintaining its position as a global leader in diabetes device innovation:
- High Prevalence of Diabetes: The unfortunate reality of a high and growing prevalence of diabetes across the U.S., influenced by lifestyle factors, aging demographics, and obesity rates, creates a significant demand for effective management tools. This large patient population acts as a powerful incentive for research and development.
- Robust Research and Development Infrastructure: The U.S. boasts a world-class ecosystem of academic institutions, research centers, and pharmaceutical and medical device companies. This environment fosters continuous innovation, attracting significant investment in diabetes technology.
- Favorable Regulatory Environment: While the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is known for its stringent approval processes, a clear pathway for medical device approvals encourages companies to bring new technologies to market. For example, the FDA’s approval of “Kirsty” (insulin aspart-xjhz) in July 2025 as the first rapid-acting interchangeable biosimilar product to Novolog, illustrate a push towards increased access and affordability, alongside device innovation.
- Strong Reimbursement Landscape: Relatively robust insurance coverage and reimbursement policies for advanced diabetes devices, including CGMs and insulin pumps, make these technologies more accessible to a broader patient population. This financial support reduces barriers to adoption and incentivizes manufacturers.
- Emphasis on Digital Health Integration: The U.S. healthcare system is increasingly embracing digital health solutions. The integration of device data with telehealth platforms, remote patient monitoring systems, and electronic health records is becoming commonplace. This digital transformation enhances care coordination and empowers individuals with more personalized insights. For example, many companies are focusing on AI-driven solutions and the integration of diabetes care with other health monitoring systems, such as tracking sleep patterns and activity levels.
- Competitive Landscape: The presence of numerous leading medical device companies in the U.S. fosters intense competition, driving continuous innovation and pushing companies to develop more accurate, user-friendly, and integrated solutions. Strategic alliances and mergers illustrate the broader dynamism in the MedTech sector and suggest a focus on expanding portfolios and capabilities, which can indirectly benefit diabetes care. For example, in February 2025, Stryker acquired Inari Medical, entering the high-growth peripheral vascular segment with innovative clot removal solutions, expanding its medical technology leadership.
Moreover, in April 2025, Zimmer Biomet acquired Paragon 28, a pioneering medical device company focused solely on the fast-growing foot and ankle orthopedic space.
The Trajectory of Device Innovation
The future of diabetes management in the U.S. appears to be one of increasing integration and personalization. The trend is moving towards even smaller, less invasive sensors for CGMs, and more discreet, tubeless options for insulin delivery. Furthermore, the convergence of artificial intelligence and machine learning promises to revolutionize predictive modeling for glucose levels and more sophisticated automated insulin delivery systems. The ongoing focus on improving patient adherence, reducing the burden of disease management, and enhancing overall quality of life will continue to fuel the remarkable device innovation seen in the U.S. diabetes market.